[Dieterich]
Hello everyone, I’m Dr Douglas Dieterich. My colleagues in this presentation are Dr Duke Nguyen and
Dr Carrie Frenette.
[Nguyen]
Thank you, Dr Dieterich. It’s great to be here today.
[Frenette]
Yes, thank you. We are excited about sharing this timely information with you!
[Dieterich]
That’s wonderful.
[Dieterich]
We are here today to discuss the latest expert guidance regarding the management of chronic hepatitis
B. This is a non-CME educational video which is sponsored by Gilead Sciences.
[Dieterich]
Today we are going to talk about the prevalence and the unmet needs for chronic hepatitis B in the US,
an overview of the Simplified Approach Hepatitis B Algorithm, a treatment overview, and then some
regional information on chronic hepatitis B in New York and California. We will then conclude with
additional resources.
[Dieterich]
First, let’s take a look at the impact of chronic hepatitis B in the whole United States.
[Dieterich]
Hepatitis B virus infection is the most common chronic viral infection in the world, causing 780,000
hepatocellular carcinoma and liver-related deaths each year.
Here in the US, it is estimated that more than 600,000 people have been diagnosed with chronic
hepatitis B infection, putting these people at risk for serious liver disease.
[Dieterich]
Despite the seriousness of this disease, chronic hepatitis B is undermanaged and undertreated. For
example, approximately 70% of patients who are diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B are not receiving
antiviral treatment. Moreover, approximately 65% of patients who have chronic hepatitis B and cirrhosis
are not receiving antiviral treatment.
We also know that more than 60% of patients with chronic hepatitis B are not receiving regular
monitoring of their chronic hepatitis B or more importantly screening for their liver
cancers.
These statistics are particularly troubling when you consider that 20 to 30% of adults with chronic
hepatitis B will develop complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
[Dieterich]
One of the most serious complications that can occur due to hepatitis B is liver cancer. The hepatitis
B virus is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, meaning that it can cause cancer in humans. Hepatitis B
virus carries the same carcinogen classification as tobacco smoking and asbestos, highlighting the
carcinogenic potential of hepatitis B. Persons with hepatitis B are at a 25- to 37-fold increased risk
of liver cancer compared to non-infected people.
[Dieterich]
Hepatitis B increases the risk of liver cancer through both direct and indirect mechanisms, which may
occur at early stages of the disease and during any phase of the hepatitis B infection.
Studies have shown that even untreated patients in the immune-tolerant phase of chronic hepatitis B are
at increased risk of liver cancer.
Hepatitis B drives liver cancer development by several processes, including integration of DNA into the
host genome, chromosomal instability, necroinflammation, and fibrosis development. It
is estimated that approximately 20% of HCC occurs in patients who do not have cirrhosis.
I have seen this in my practice, as I have a female patient with chronic hepatitis B who presented at
the age of 29 with no cirrhosis but with a liver cancer.
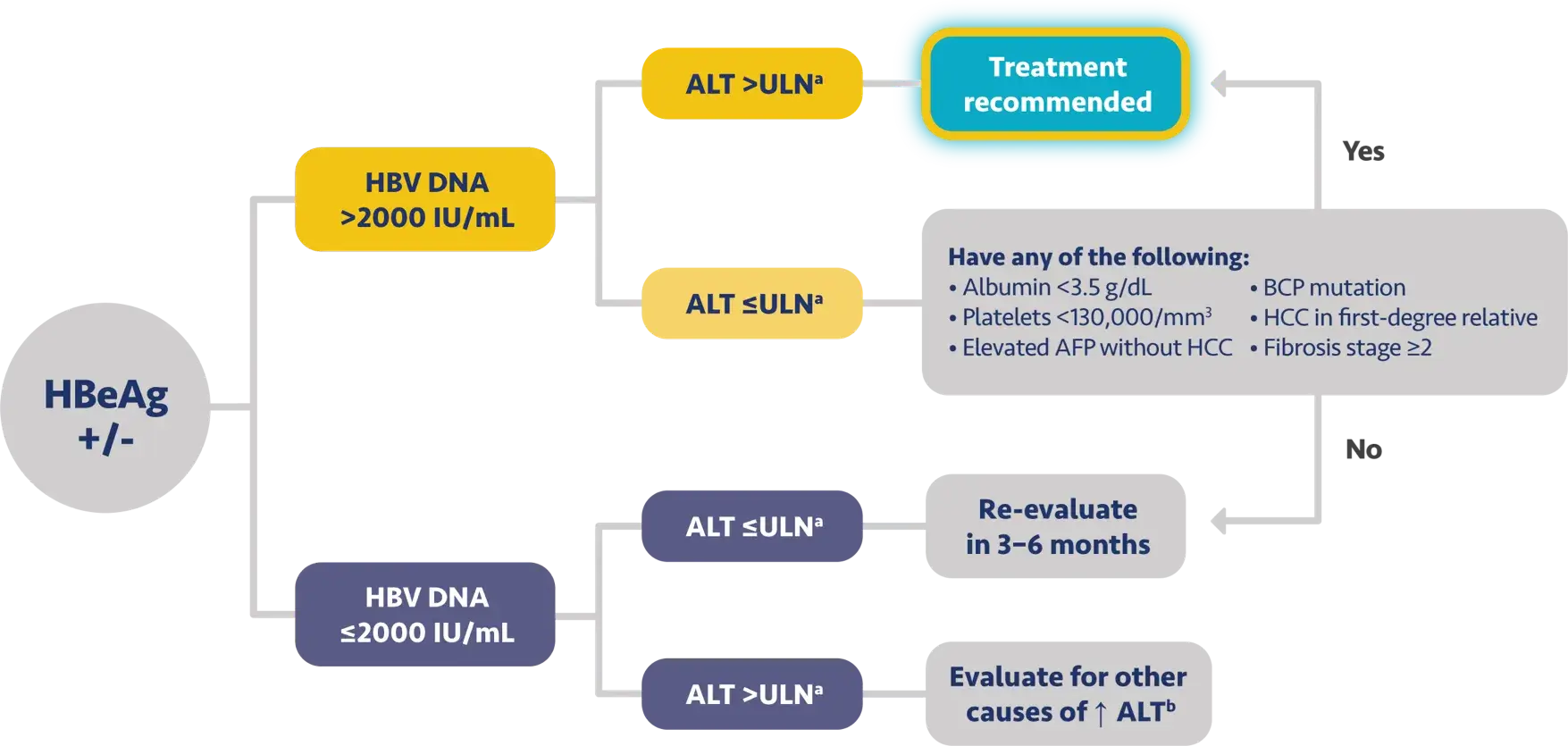
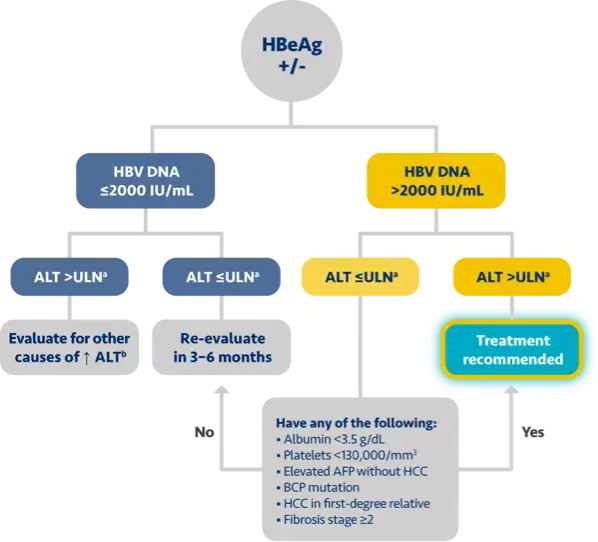
One of the key determinants of the oncogenicity of hepatitis B infection is the level of HBV DNA.
Studies have shown that HBV DNA levels above 2000 are associated with an increased risk of HCC and this
risk is present even in patients without elevated ALT levels.
These parameters are important to keep in mind as we consider which patients with chronic hepatitis B
should be recommended for antiviral therapy.
[Dieterich]
Now, I’d like to introduce you to the latest expert guidance for chronic hepatitis B treatment, the
Simplified Approach Hepatitis B Algorithm, or SABA.
[Dieterich]
The current HBV guidelines and algorithms are directed toward specialists and can be rather complex. As
we reviewed in the introduction, data show there are significant gaps in care for patients with
hepatitis B.
Because of this, a group of 7 other experts and myself, spanning hepatology, infectious disease,
primary care developed a streamlined algorithm of hepatitis B intervention, encouraging earlier
treatment for appropriate patients.
Our publication includes the rationale for the algorithm along with recommendations on screening for
hepatitis B infection, diagnostic work up, antiviral treatment, and monitoring of patients.
[Dieterich]
The members of our expert panel, shown here, included Drs Agarwal, Kwo, and Lim, who are
hepatologists; Dr Graham and Sulkowski, who are infectious disease specialists; and Drs Liu and Wang,
who are primary care physicians. We published our recommendations in Gastro Hep Advances. If you scan
this QR code, it will take you to our published article.
[Dieterich]
The goal of our global expert panel was to gain consensus on a streamlined approach to hepatitis B care
in order to facilitate implementation of hepatitis B intervention and treatment, especially in the
primary care setting.
[Dieterich]
Notably, our approach was to assume that all patients with chronic hepatitis B need to be treated, and
then to exclude those who do not ‘qualify’ for treatment, rather than the currently prevailing, reverse
perspective. The goal is to reduce the number of patients who are not receiving appropriate
treatment.
[Dieterich]
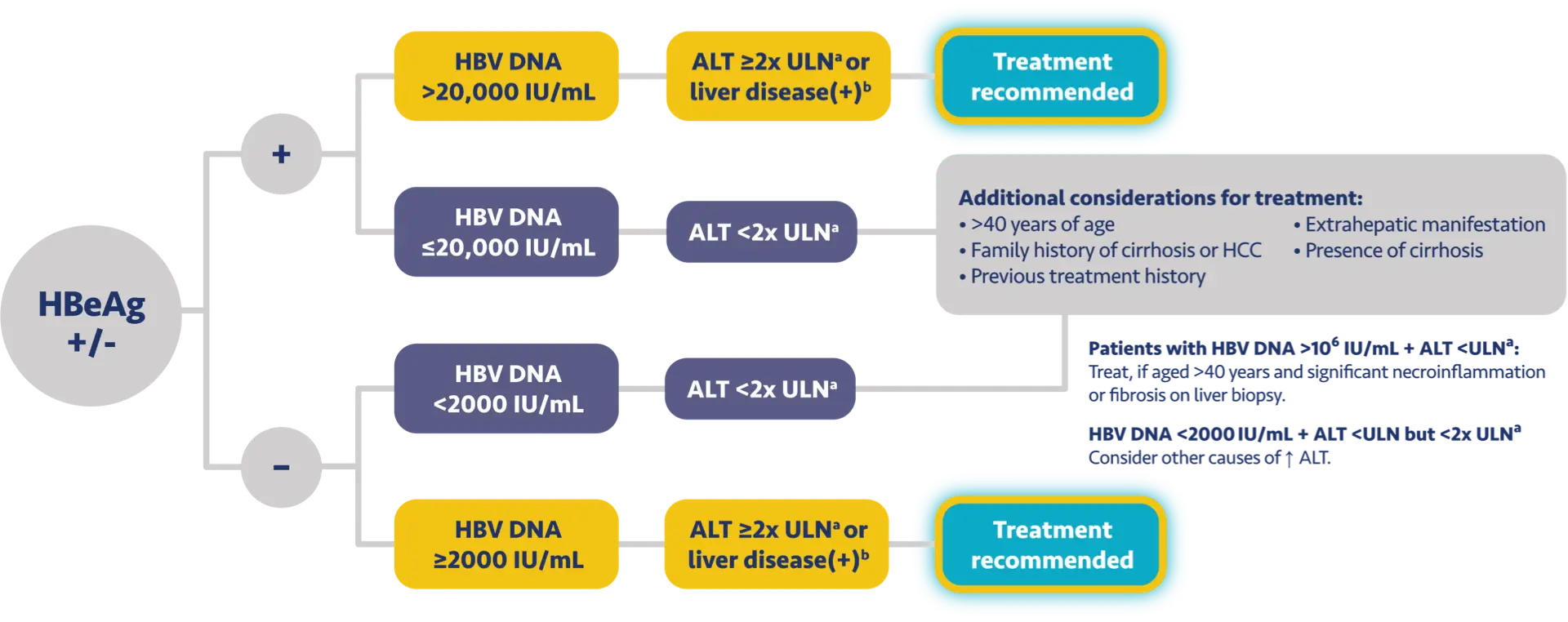
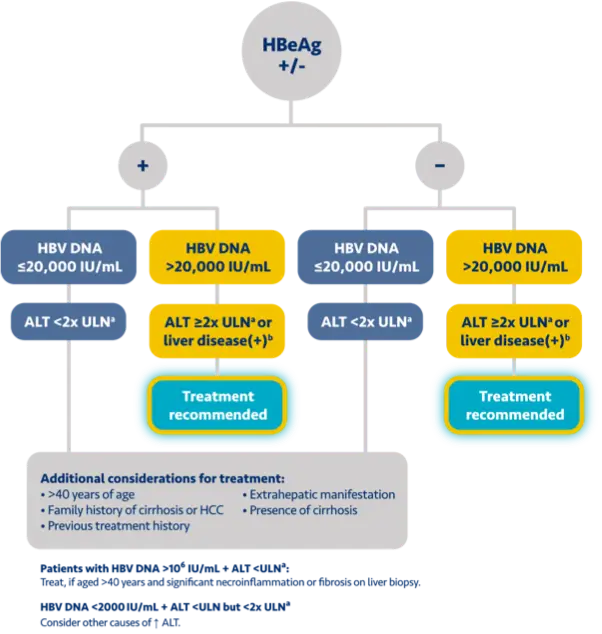
Here is the treatment algorithm that we developed. First, all patients with compensated cirrhosis and
any HBV DNA should receive antiviral treatment, regardless of ALT levels.
[Dieterich]
In addition, patients who are at least 30 years old, with HBV DNA >2000 IUs should receive antiviral
treatment, regardless of ALT level.
[Dieterich]
For adults who are younger than 30 years old, the recommendation is to start treatment if they have HBV
DNA >2000 plus ALT above the upper limit of normal, which we defined as 30 for men and 19 for
women.
[Dieterich]
These treatment criteria are based on research that shows that patients who are older than 30 and have
elevated DNA are at risk for liver disease progression. This age cut off of 30 years old is also
recommended by the World Health Organization as a treatment criterion for antiviral therapy.
In addition, there is clinical evidence demonstrating that HBV DNA levels of >2000 IUs are associated
with an increased risk of HCC or progression to cirrhosis, regardless of e antigen status or ALT
level.
In discussions with healthcare providers about this algorithm, I’ve been asked if I have concerns about
treatment adherence, especially in such young patients, but in my experience, even patients who are in
their 20s and 30s remain adherent when they understand the seriousness of hepatitis B.
I will now turn this over to my colleague, Dr Nguyen.
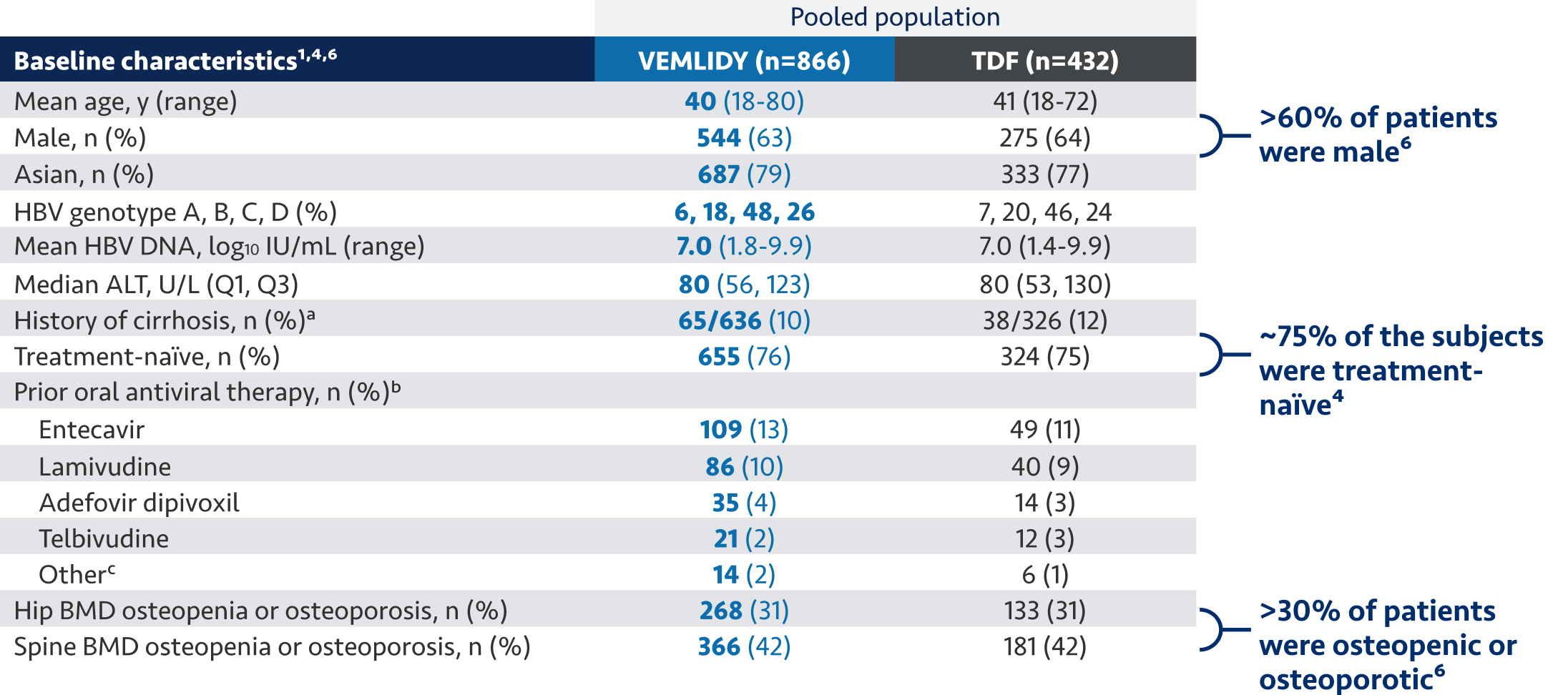
[Nguyen]
Now, we would like to discuss the use of VEMLIDY.
VEMLIDY is indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection in adults with compensated
liver disease.
VEMLIDY carries a Boxed Warning for posttreatment severe acute exacerbation of hepatitis B.
Discontinuation of anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VEMLIDY, may result in severe acute
exacerbations of hepatitis B. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and
laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who discontinue anti-hepatitis B therapy,
including VEMLIDY. If appropriate, resumption of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted.
Please stay tuned at the end of this video Dr Carrie Frenette will review additional important safety
considerations for VEMLIDY.
[Nguyen]
VEMLIDY is recommended as a first-line hepatitis B therapy by the Simplified Approach to Hepatitis B
Algorithm, and by the guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the US
Treatment Algorithm, the Asian American Treatment Algorithm, and the guidelines from the European
Association for the Study of the Liver.
[Nguyen]
The guidelines and algorithms recommend VEMLIDY as a first-line therapy because it has proven efficacy,
0 resistance, and demonstrated reduced impact on long-term renal and bone safety
parameters. Although, long-term clinical significance of these have not yet been fully
quantified.
Therefore, VEMLIDY can be considered in patients with, or at risk for, renal dysfunction and bone
disease.
Postmarketing cases of renal impairment, including acute renal failure and proximal renal tubulopathy,
have been reported. In all patients, monitor renal function and discontinue treatment in those who
exhibit significant reductions in renal function or evidence of Fanconi syndrome.
VEMLIDY is not recommended in patients with end stage renal disease, who are not receiving chronic
hemodialysis. In patients on chronic hemodialysis, on dialysis days, VEMLIDY should be administered
after the completion of hemodialysis.
[Nguyen]
So Dr Dieterich, can you tell us more about your experiences with hepatitis B in your region and your
management of these patients?
[Dieterich]
Sure, Duke.
[Dieterich]
My practice is in New York City, and many people don’t realize that approximately 22% of the people in
New York are immigrants, including people from places with higher endemicity of chronic hepatitis B,
such as Asia and Africa. More than half of New Yorkers live in households with at least one
immigrant.
[Dieterich]
About 3% of New York City residents are living with hepatitis B. As shown in this graph,
the boroughs with the highest incidence are Brooklyn and Queens, followed by the Bronx, Manhattan, and
last, Staten Island. In addition, it has been estimated that 46% of New York City residents
with hepatitis B remain undiagnosed. So as you can see, chronic hepatitis B has an
important impact in New York.
[Dieterich]
The SABA recommendations are particularly applicable to my practice in New York. For example, I
regularly see patients with chronic hepatitis B who are in their 30s and have elevated hepatitis B DNA,
but have normal ALT levels. My recommendation is to treat these patients with antiviral therapy, as
described in the overview of the SABA algorithm.
I have a discussion with my patients about the importance of antiviral therapy and how oral antivirals
can fit well with their routine. With the appropriate understanding and motivation, the majority of my
patients remain on therapy as indicated, including younger patients, such as adults younger than 30
years old. For example, I have an 18-year-old male patient with chronic hepatitis B who is so dedicated
to taking his medicine that he proactively told me about his plans for taking his VEMLIDY during a
week-long ski vacation.
For all my patients, I ensure that they understand the potential adverse reactions for VEMLIDY, with
headaches being the most common.
[Dieterich]
Before initiating therapy, I make sure to set expectations with my patients for testing and monitoring.
This includes before starting treatment with VEMLIDY, and during treatment, patients should have their
creatinine levels, urine glucose, and urine protein tested. For those with chronic kidney disease they
should also have their serum phosphorus assessed. If patients discontinue VEMLIDY treatment, it's important to closely monitor their hepatic function for at least several months after stopping
treatment.
In addition to these monitoring requirements, the expert panel recommends that patients come in for a
clinic visit every 3 months until viral suppression is achieved, then every 6 months
thereafter. Every 6 months we conduct a liver ultrasound and test their level of
alpha-fetoprotein. We also regularly assess their creatinine clearance.
Some of my colleagues have asked about insurance access or coverage for VEMLIDY. I’ve been able to get
insurance coverage for my patients on VEMLIDY, although coverage can differ for other providers and
patients. If my patients have questions about how to access VEMLIDY, I point them to the VEMLIDY.com
website where they can learn about the co-pay program and Support Path.
[Dieterich]
Now, I’d like to pass things over to Dr Nguyen to tell us about chronic hepatitis B in California and
his experience in managing patients there.
[Nguyen]
Thank you, Dr Dieterich. Although New York and California are on opposite sides of the country, we in
California do share a lot in common with you in New York as it relates to chronic hepatitis B being an
important health concern.
[Nguyen]
California is home to almost 11 million immigrants, which represents approximately 25% of the
first-generation immigrants in the US. This includes people from high hepatitis B endemic areas, such
as Asia and Africa.
[Nguyen]
The prevalence of chronic hepatitis B is particularly high in California, with Asian Pacific Islanders
being especially at risk. In San Francisco Bay Area, hepatitis B-related hepatocellular
carcinoma is a leading cause of death among Asian Pacific Islanders. In addition, the
prevalence of people with chronic hepatitis B is estimated to be more than 2-fold higher in the Los
Angeles County compared with the US overall.
So, just as hepatitis B infection is an important public health concern globally, this is also true for
California.
[Nguyen]
My practice is in Fountain Valley, in southern California, where we see many patients with chronic
hepatitis B, including some with hepatocellular carcinoma without signs of cirrhosis. These are the 20%
of patients that Dr Dieterich mentioned earlier, which is what makes this a particularly insidious
disease.
I think we’re fortunate in our area that we have many physicians who are very passionate about
hepatitis B therapy, including primary care providers who have been educated throughout the years and
some of them have taken it upon themselves to help in the management.
This is a segue to one of my favorite English sayings, if you give a man a fish, you will feed him for
a day. Teach a man to fish, you will feed him for a lifetime.
So I educate my primary care providers to be comfortable to treat hepatitis B so they can take care of
their patients. If they are not comfortable, I will manage the patient with them.
I believe the Simplified Approach to Hepatitis B Algorithm will support antiviral therapy for many
adult patients who would benefit from it and who may not otherwise be recommended based on other
guidance. This is a step forward for our chronic hepatitis B patients.
[Nguyen]
In my personal experience, patients have had success obtaining insurance coverages for VEMLIDY when we
have prescribed it.
I have referred patients to the VEMLIDY Co-pay Coupon Program. For some eligible patients, their
co-pays were as low as $0.
And now, I would like to introduce Dr Carrie Frenette who will provide more information on these
resources. Dr Frenette.
[Frenette]
Thank you, Dr Nguyen.
[Frenette]
Gilead has support resources for patients with chronic hepatitis B. With the VEMLIDY Co-pay Coupon
Program, eligible patients with commercial insurance may pay as low as a $0 co-pay for out-of-pocket
costs for VEMLIDY, up to $6000 per year with no monthly limit.
Support Path can help patients to understand their coverage and identify financial support options. To
learn more, visit mysupportpath.com, and for multilingual assistance, call 1-855-769-7284, Monday
through Friday, between 9 am and 8 pm Eastern Standard Time. These are subject to change and
restrictions apply. See the full terms and conditions at mysupportpath.com/providers.
[Frenette]
Now, let’s review some additional Important Safety Information for VEMLIDY.
[Frenette]
Warnings and Precautions
Risk of Development of HIV-1 Resistance in HBV/HIV-1 Coinfected Patients: Due to this risk, VEMLIDY
alone should not be used for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Safety and efficacy of VEMLIDY has not
been established in HBV/HIV-1 coinfected patients. HIV antibody testing should be offered to all
HBV-infected patients before initiating therapy with VEMLIDY, and, if positive, an appropriate
antiretroviral combination regimen that is recommended for HBV/HIV-1 coinfected patients should be used.
New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment: Postmarketing cases of renal impairment, including acute renal
failure, proximal renal tubulopathy (PRT), and Fanconi syndrome have been reported with TAF-containing
products. Patients with impaired renal function and/or taking nephrotoxic agents (including NSAIDs) are
at increased risk of renal-related adverse reactions. Discontinue VEMLIDY in patients who develop
clinically significant decreases in renal function or evidence of Fanconi syndrome. Monitor renal
function in all patients – See Dosage and Administration.
Lactic Acidosis and Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis: Fatal cases have been reported with the use of
nucleoside analogs, including tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF). Discontinue VEMLIDY if clinical or
laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity develop, including
hepatomegaly and steatosis in the absence of marked transaminase elevations.
[Frenette]
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%; all grades) in clinical studies through week 144
were headache, upper respiratory tract infection, abdominal pain, cough, back pain, arthralgia, fatigue,
nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, and pyrexia.
Drug Interactions
Coadministration of VEMLIDY with drugs that reduce renal function or compete for active tubular
secretion may increase concentrations of tenofovir and the risk of adverse reactions.
Coadministration of VEMLIDY is not recommended with the following: oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital,
phenytoin, rifabutin, rifampin, rifapentine, or St. John’s wort. Such coadministration is expected to
decrease the concentration of tenofovir alafenamide, reducing the therapeutic effect of VEMLIDY. Drugs
that strongly affect P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) activity may lead
to changes in VEMLIDY absorption.
Consult the full prescribing information for VEMLIDY for more information on potentially significant
drug interactions, including clinical comments.
Dosage and Administration
Testing Prior to Initiation: should include HIV infection.
Prior to or When Initiating, and During Treatment: On a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum
creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. In
patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus.
The Dosage in Adults: is 1 tablet taken once daily with food.
Renal Impairment: It’s not recommended in patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD; estimated
creatinine clearance <15 mL/min) who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis; in patients on chronic
hemodialysis, on hemodialysis days, administer VEMLIDY after completion of hemodialysis treatment.
Hepatic Impairment: Not recommended in patients with decompensated (Child-Pugh B or C) hepatic
impairment.
[Dieterich]
Thank you for joining us today for this discussion about SABA recommendations and how earlier treatment
may be an option for your appropriate adult chronic hepatitis B patients.
[Nguyen]
Thanks, Doug. And yes, thank you for joining us, we hope that today’s video will aid you in the
management of your chronic hepatitis B patients.
[Frenette]
Thanks so much for joining us!